Dynamic Variables
Dynamic variables let you configure a template for your agent's behavior. You can re-use the same general instructions while dynamically personalizing every conversation your agent has.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to:
- Template your AI assistant configuration with dynamic variables.
- Supply the values via an outbound API request or the dynamic variable webhook.
Overview
Dynamic variables enable you to create a single AI assistant configuration that can handle personalized conversations for different users and contexts. Instead of creating multiple assistants for different scenarios, you can use placeholders that get filled with specific values at runtime.
How dynamic variables work
The dynamic variable lifecycle follows these steps:
- Define: Create placeholders in your assistant's instructions, greeting, or tools using
{{variable_name}}syntax. - Inject: Provide values through API calls, webhooks, SIP headers, or default configurations.
- Resolve: Telnyx replaces placeholders with actual values when the conversation starts.
- Use: Your assistant uses the personalized content throughout the conversation.
Key benefits
- Scalability: One assistant configuration serves multiple use cases.
- Personalization: Each conversation can be tailored to specific users or contexts.
- Efficiency: Reduce configuration overhead and maintenance complexity.
- Flexibility: Update values dynamically without modifying the assistant.
Common use cases
- Customer Service: Personalize greetings with customer names and account details.
- Appointment Scheduling: Include facility names, departments, and contact information.
- Account Management: Reference specific account numbers, balances, or service details.
- Healthcare: Customize interactions with patient names, appointment types, and provider information.
Best practices
Following these best practices will help you implement dynamic variables effectively and avoid common pitfalls.
Variable naming and organization
- Use descriptive names: Choose clear, meaningful variable names like
customer_nameinstead of generic names likename. - Follow consistent conventions: Use snake_case for variable names (
facility_name,account_number). - Group related variables: Organize logically related variables together (
facility_name,facility_department,facility_contact). - Avoid reserved namespaces: Don't use the
telnyx_prefix, which is reserved for system variables.
// Good variable naming
{
"customer_name": "Sarah Johnson",
"account_number": "ACC-12345",
"facility_name": "Memorial Hospital",
"facility_department": "Cardiology"
}
// Poor variable naming
{
"name": "Sarah",
"num": "12345",
"place": "Hospital",
"dept": "Card"
}
Implementation strategy
- Start with defaults: Set default values in the Assistant builder for testing and as fallback values.
- Use API injection for dynamic data: Pass call-specific values through the
AIAssistantDynamicVariablesparameter in API calls. - Leverage webhooks for complex lookups: Use the dynamic variables webhook for real-time data retrieval or database lookups.
- Implement graceful degradation: Ensure your assistant can handle scenarios where variables fail to resolve.
Security and data handling
- Protect sensitive information: Be cautious about including sensitive data in variables that may appear in logs.
- Validate webhook data: Implement proper validation for data returned from webhook endpoints.
- Consider data retention: Review your data retention and privacy requirements for variable content.
- Handle timeouts gracefully: Webhook responses must return within 1 second or the call proceeds with fallback values.
Performance and reliability
- Optimize webhook response time: Keep webhook responses fast (well under the 1-second timeout).
- Implement error handling: Plan for scenarios where webhooks fail or return invalid data.
- Use caching strategies: Cache frequently accessed data to improve response times.
- Test across channels: Verify variable resolution works consistently across phone calls, web calls, and SMS.
Testing and debugging
- Test with Portal defaults: Use the Assistant builder's default values to test variable behavior during development.
- Monitor webhook logs: Use the conversation transcript and webhook logs in the Portal to debug variable resolution issues.
- Validate fallback behavior: Ensure unresolved variables (displayed as
{{variable_name}}) don't break conversation flow. - Test transfer scenarios: Verify that variables pass correctly when using transfer tools with SIP headers.
Cross-channel considerations
- Ensure universal compatibility: Test that your variables work across phone calls, web calls, and SMS channels.
- Handle channel-specific data: Consider how variables might behave differently across conversation channels.
- Plan for transfer scenarios: When transferring calls, use SIP headers to pass variable data to the receiving assistant.
Dynamic variables syntax
Dynamic variables are placeholders surrounded by double curly braces. For example:
Hello, this is ABC Ambulance. Am I speaking with {{full_name}} with {{facility_name}} - {{facility_department}}?"
You can template them in the following fields:
- Instructions
- Greeting
- Tools
Telnyx system variables
Telnyx also provides these system variables:
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
{{telnyx_current_time}} | The current date and time in UTC | Monday, February 24 2025 04:04:15 PM UTC |
{{telnyx_conversation_channel}} | This can be phone_call , web_call, or sms_chat | phone_call |
{{telnyx_agent_target}} | The phone number, SIP URI, or other identifier associated with the agent. | +13128675309 |
{{telnyx_end_user_target}} | The phone number, SIP URI, or other identifier associated with the end user | +15551234567 |
{{call_control_id}} | The call control ID for the call, if applicable | v3:u5OAKGEPT3Dx8SZSSDRWEMdNH2OripQhO |
Customer-defined dynamic variables
You can also define your own variables. There are several ways to resolve a customer-defined dynamic variable before a conversation. They follow this order of precedence.
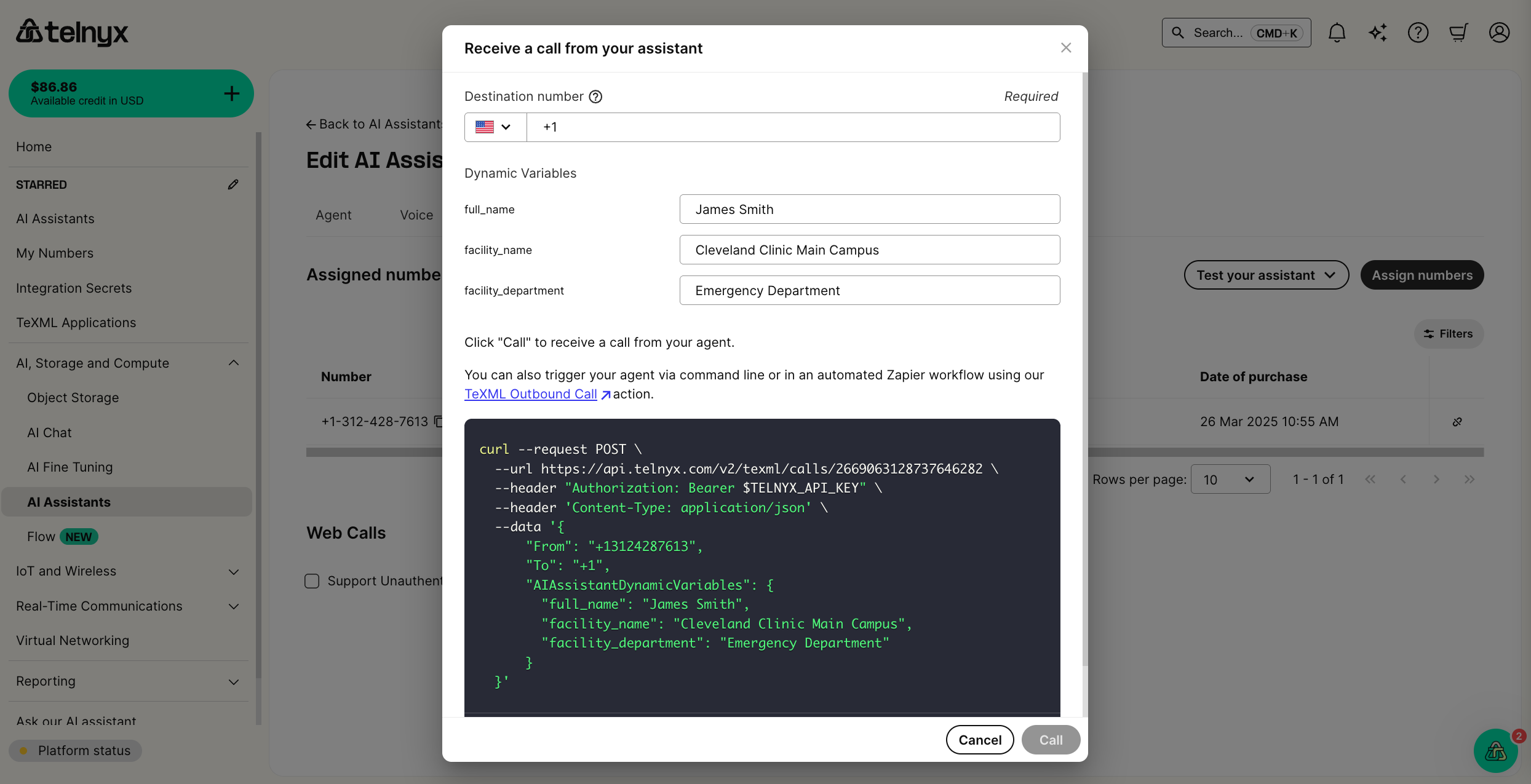
1. Pass the variables via the outbound API call
curl --request POST \
--url https://api.telnyx.com/v2/texml/calls/<texml_app_id> \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $TELNYX_API_KEY" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"From": "+13128675309",
"To": "+15551234567",
"AIAssistantDynamicVariables": {
"full_name": "James Smith",
"facility_name": "Cleveland Clinic Main Campus",
"facility_department": "Emergency Department"
}
}'
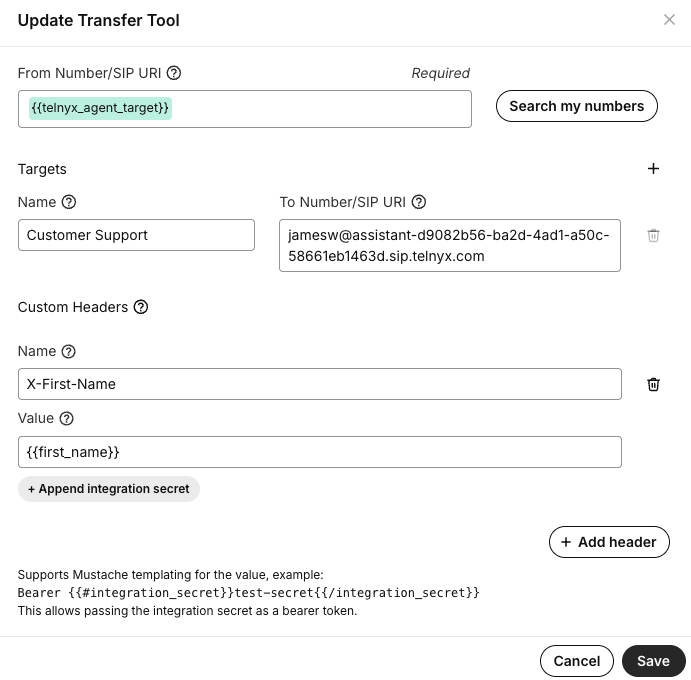
2. Custom SIP Headers
Custom SIP headers using the X- prefix will be mapped to dynamic variables. Header names are case-insensitive, and - in the header names will be replaced by _ in the variable names.
For instance, X-Full-Name will be resolved as {{full_name}}.
Telnyx reserves the {{telnyx_}} namespace for system variables, meaning SIP headers beginning X-Telnyx will not be resolved to dynamic variables.
Here you can see an example of passing a dynamic variable to another AI Assistant using custom SIP headers in the Transfer tool.
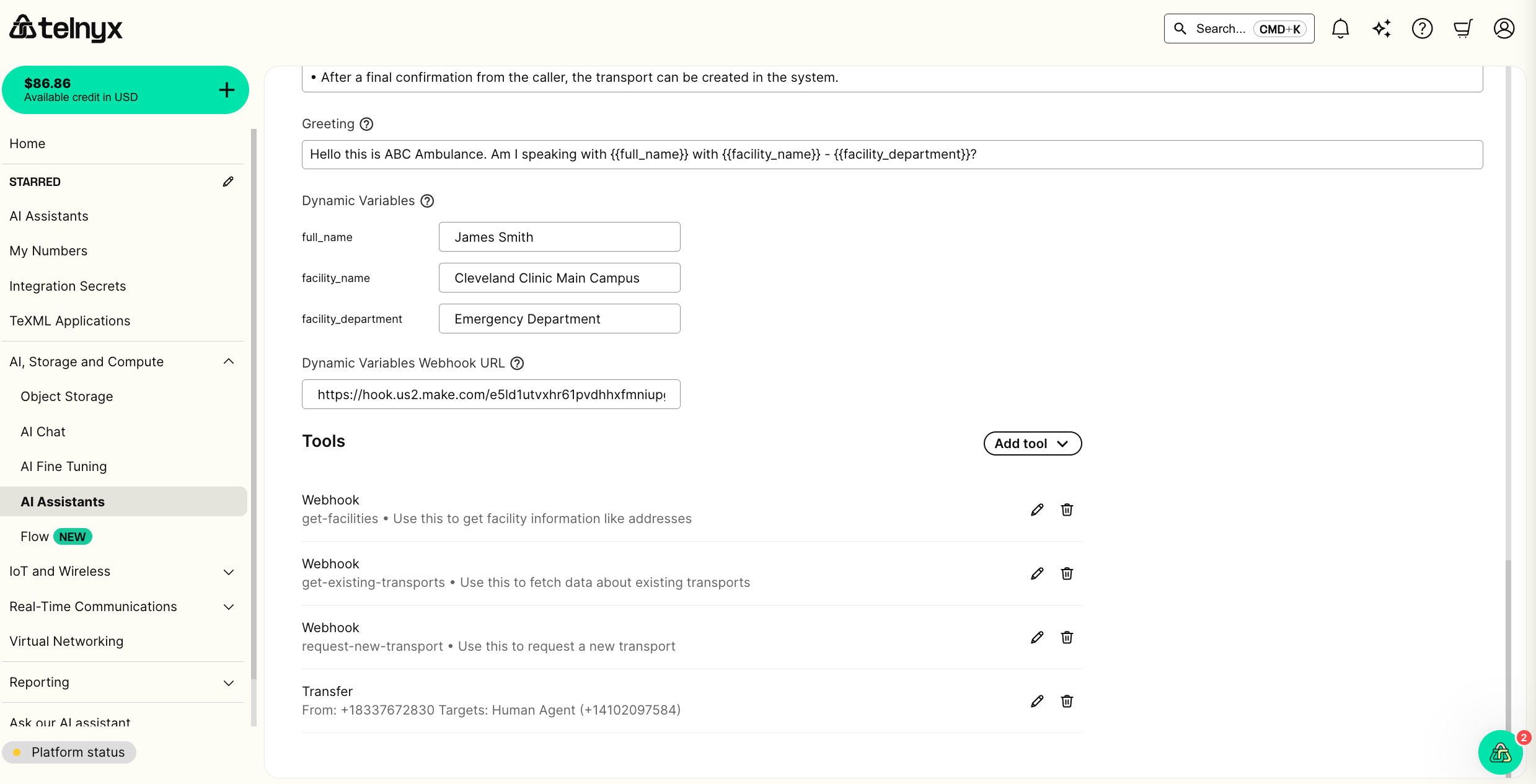
3. Configure Dynamic Variables Webhook
If the dynamic_variables_webhook_url is set for the assistant, we will POST the following payload at the start of the conversation. Telnyx will sign this webhook so that the authenticity of the request can be verified.
{
"data": {
"record_type": "event",
"id": "event_12345678-90ab-cdef-1234-567890abcdef",
"event_type": "assistant.initialization",
"occurred_at": "2025-04-07T10:00:00Z",
"payload": {
"telnyx_conversation_channel": "phone_call",
"telnyx_agent_target": "+13128675309",
"telnyx_end_user_target": "+15551234567",
"telnyx_end_user_target_verified": false,
"call_control_id": "v3:u5OAKGEPT3Dx8SZSSDRWEMdNH2OripQhO",
"assistant_id": "assistant_12345678-90ab-cdef-1234-567890abcdef"
}
}
}
For inbound phone calls to an assistant, the telnyx_end_user_target_verified field will be set to true if the call has Full (A) STIR/SHAKEN attestation and Telnyx was able to verify the authenticity of the PASSporT token.
We expect a JSON response with the following structure. If we do not receive this response within a 1-second timeout, the call will proceed "best effort" with the alternatives listed below.
All three fields (dynamic_variables, memory, and conversation) are optional. The dynamic_variables field sets the values for the specified dynamic variables.
You can read more about the memory and conversation fields in our tutorial on Memory.
{
"dynamic_variables": {
"full_name": "Rachel Thomas",
"facility_name": "UCHealth",
"facility_department": "Cardiology",
"account_number": "ACC-12345",
"appointment_time": "2:30 PM"
},
"memory": {
"conversation_query": "metadata->telnyx_end_user_target=eq.+13128675309&limit=5&order=last_message_at.desc"
},
"conversation": {
"metadata": {
"customer_tier": "premium",
"preferred_language": "en",
"timezone": "America/Denver"
}
}
}
4. Configure default dynamic variables in the Assistant builder
In the above view, you can also set default values for dynamic variables at the agent level. These will serve as a fallback if any of the above mechanisms do not properly resolve a variable.
5. Unset variables
Variables not set by any of the above methods will remain in their raw form ({{full_name}}).
Troubleshooting
Dynamic variables can sometimes fail to resolve or behave unexpectedly. This section provides comprehensive guidance for identifying and resolving common issues.
Common issues
Variables not resolving
When variables appear as raw text ({{variable_name}}) in conversations, check these potential causes:
- Webhook timeout: Your webhook endpoint took longer than 1 second to respond, causing fallback to defaults.
- Variable name mismatch: Typos or case sensitivity differences between variable definition and usage.
- Incorrect precedence: Understanding the resolution order (API > SIP headers > webhook > defaults).
- Missing configuration: Variable not defined in any resolution method.
Incorrect formatting
Variables may not work correctly due to formatting issues:
- Invalid JSON: Webhook responses contain malformed JSON syntax.
- Wrong data types: Sending numbers instead of strings or vice versa.
- Missing required fields: Webhook response missing
dynamic_variablesobject. - Template syntax errors: Incorrect mustache template usage (
{variable}instead of{{variable}}).
Timeout issues
Webhook timeouts are a common source of variable resolution failures:
- Slow database queries: Optimize database lookups in webhook endpoints.
- Network connectivity: Check firewall rules and network connectivity to webhook URLs.
- External service delays: Implement proper timeout handling for third-party API calls.
- Processing overhead: Minimize computation time in webhook response generation.
Debugging checklist
Follow this step-by-step process to diagnose variable issues:
1. Verify variable definition
- Check variable name spelling and case sensitivity.
- Confirm variables are used in supported fields (
instructions,greeting,tools). - Validate mustache syntax:
{{variable_name}}. - Ensure variable names don't use reserved
telnyx_prefix.
2. Check resolution priority
Test variables using the resolution hierarchy:
# Test API injection (highest priority)
curl --request POST \
--url https://api.telnyx.com/v2/texml/calls/<texml_app_id> \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $TELNYX_API_KEY" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"From": "+13128675309",
"To": "+15551234567",
"AIAssistantDynamicVariables": {
"test_variable": "API_VALUE"
}
}'
- Verify SIP header format for transfer scenarios:
X-Variable-Namebecomes{{variable_name}}. - Confirm webhook endpoint is reachable and responding correctly.
- Set default values in Assistant builder as fallback.
3. Validate webhook implementation
- Test webhook endpoint independently using tools like Postman.
- Verify JSON response format matches expected structure.
- Check response time (must be under 1 second).
- Validate all required payload fields are present.
4. Test in Portal
- Use Assistant builder default values for initial testing.
- Review conversation logs for variable resolution behavior.
- Check webhook logs for errors, timeouts, or unexpected responses.
Webhook debugging
Using webhook logs effectively
To facilitate troubleshooting webhook issues, logs are viewable per conversation in the portal alongside the conversation transcript and insights.
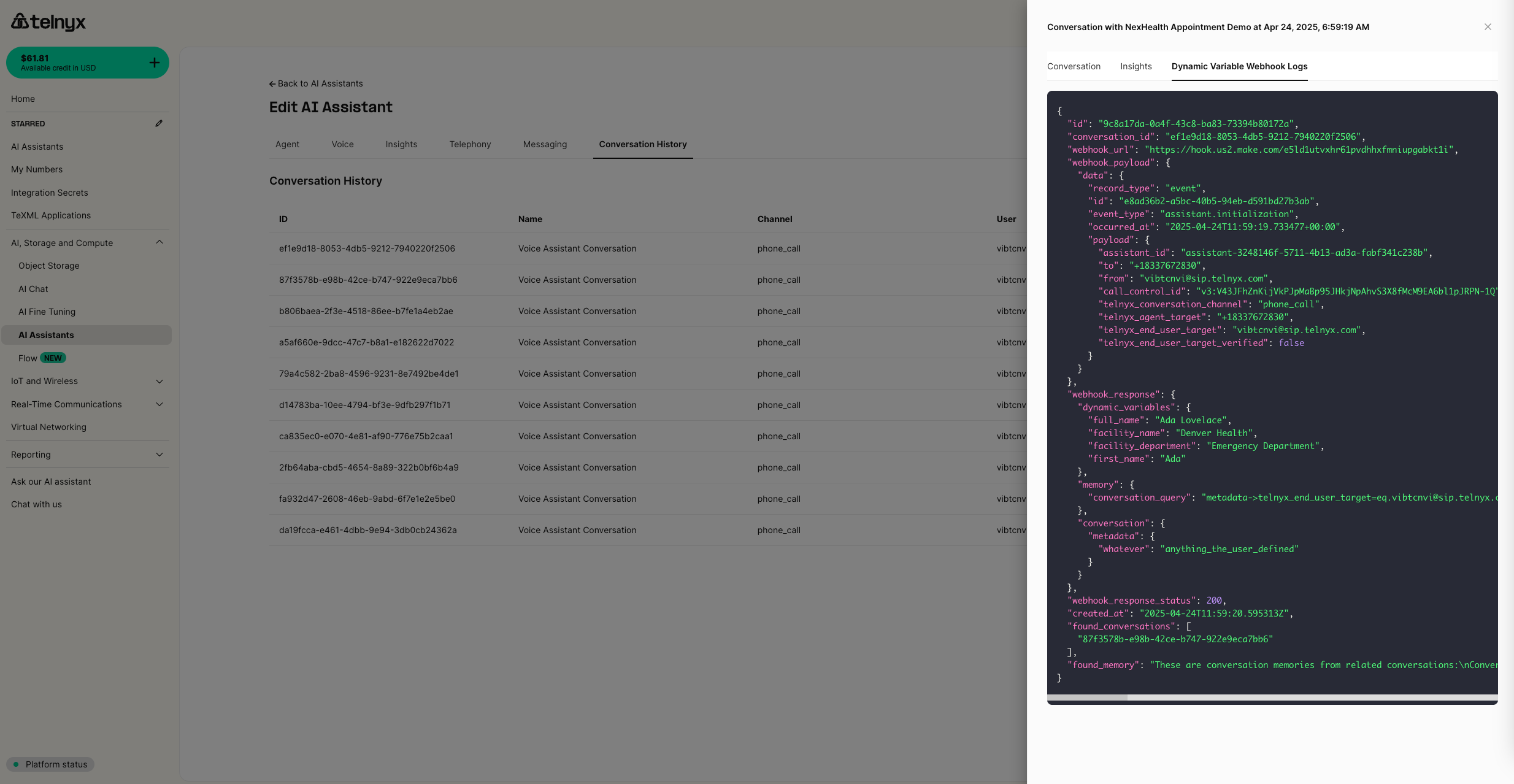
Understanding webhook logs:
- Request logs: Show the exact payload Telnyx sent to your webhook
- Response logs: Display your webhook's response and any errors
- Timing information: Reveals if responses exceeded the 1-second timeout
- Error details: Provide specific error messages for failed requests
Common webhook issues
Authentication failures:
// Webhook response indicating auth failure
{
"error": "Unauthorized: Invalid API key",
"dynamic_variables": {}
}
Malformed JSON responses:
// Incorrect - missing quotes around keys
{
dynamic_variables: {
customer_name: "John Doe"
}
}
// Correct JSON format
{
"dynamic_variables": {
"customer_name": "John Doe"
}
}
Timeout handling:
// Webhook response for timeout scenarios
{
"dynamic_variables": {
"customer_name": "Default Name"
},
"message": "External service timeout, using cached data"
}
Testing webhook endpoints
Independent webhook testing:
# Test your webhook with the exact payload Telnyx sends
curl --request POST \
--url https://your-webhook-url.com/dynamic-variables \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"data": {
"record_type": "event",
"id": "event_12345678-90ab-cdef-1234-567890abcdef",
"event_type": "assistant.initialization",
"occurred_at": "2025-04-07T10:00:00Z",
"payload": {
"telnyx_conversation_channel": "phone_call",
"telnyx_agent_target": "+13128675309",
"telnyx_end_user_target": "+15551234567",
"call_control_id": "v3:test-call-control-id"
}
}
}'
Variable validation
Input validation
Sanitize variable values:
// Good - Clean, safe variable values
{
"dynamic_variables": {
"customer_name": "John Smith",
"account_number": "ACC-12345",
"appointment_time": "2:30 PM"
}
}
// Avoid - Potentially problematic values
{
"dynamic_variables": {
"customer_name": "<script>alert('xss')</script>",
"account_number": "'; DROP TABLE users; --",
"appointment_time": null
}
}
Handle special characters properly:
- Escape quotes and backslashes in variable content.
- Validate data types match expected formats.
- Provide meaningful defaults for empty or null values.
Response format validation
Ensure proper JSON structure:
// Complete webhook response format
{
"dynamic_variables": {
"customer_name": "Sarah Johnson",
"facility_name": "Memorial Hospital"
},
"memory": {
"conversation_query": "metadata->customer_id=eq.12345"
},
"conversation": {
"metadata": {
"customer_tier": "premium"
}
}
}
Testing scenarios
Cross-channel testing:
- Verify variables work consistently across phone calls, web calls, and SMS.
- Test variable behavior in transfer scenarios using SIP headers.
- Validate fallback behavior when webhook endpoints are unavailable.
Load testing:
- Test webhook endpoint performance under expected call volumes.
- Verify response times remain under 1 second during peak usage.
- Monitor for memory leaks or performance degradation over time.